JAVA Programming
[87] Multi Thread 임계영역 , 동기화 2가지 방법(메소드,블록)
꾸준히개발하자
2020. 8. 4. 03:34
Multi Thread 구현하기
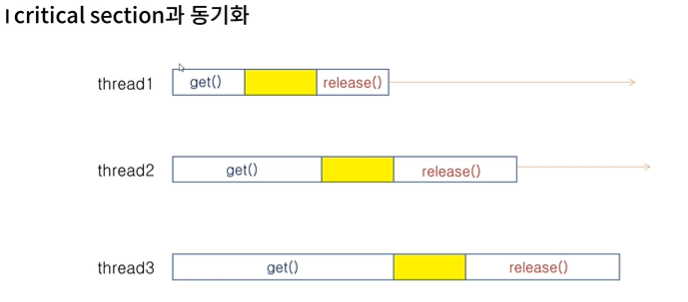
임계영역(critical section) 이란 ?
두개 이상의 thread가 동시에 접근하게 되는 리소스이다.
Critical section 에 도싱에 thread가 접근하게 되면 실행 결과를 보장할수없다.
thread간의 순서를 맞추는 동기화 (synchronization)이 필요하다.
동기화(synchronization)
임계영역에 여러 thread 가 접근하는 경우 한 thread가 수행하는 동안 공유자원을 lock 하려
다른 thread의 접근을 막는다.
동기화를 잘못 구현하면 deadlock에 빠질수 있다.
자바에서 공유자원이 되는건 static 키워드를 가진 객체인데
멤버 변수들은 static 은 공유를 하게된다 static 키워드 를 가진 객체를 공유하면
문제가 발생하게되는데 예제를 통해 보자
package thread;
class Bank {
private int money = 10000;
public void saveMoney(int save) { // 저축
int m = this.getMoney(); // 돈을 가져온다.
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setMoney(m + save);
}
public void minuMoney(int minus) { // 소비
int m = this.getMoney();
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setMoney(m - minus); // 가지고 있는 돈에서 빼준다.
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
}
class Park extends Thread {
// 출근
public void run() {
// 돈을 저금한다
System.out.println("start save");
SyncTest.myBank.saveMoney(3000); // 3천원저금
System.out.println("save money" + SyncTest.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
class ParkWife extends Thread {
public void run() {
// 돈을 사용한다.
System.out.println("start minus");
SyncTest.myBank.minuMoney(1000); // 천원저금
System.out.println("minus money" + SyncTest.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
public class SyncTest {
public static Bank myBank = new Bank();
// 은행 하나 생성 , static 으로 사용해서 클래스로 접근 가능
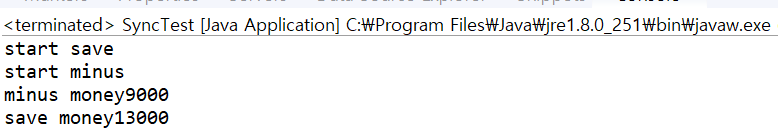
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Park p = new Park();
p.start();
Thread.sleep(200); // Park 이 저축하고나서 0.2초 후에 와이프가 시작
// 위에 Thread.sleep(3000); 3초동안 쉰동안 와이프가 시작을 해버렸기 때문이다.
// 박씨와이프는 초기화값 만원을 가져왔기 떄문이다.
// 임계영역이 bank 가 되는데 리소스가 share 가 됐는데 share 가 된상태에 순서가 안맞았기때문
// 동기화를 해주면 된다.
// 수행문 방식과 메소드 방식이 있다.
ParkWife pw = new ParkWife();
pw.start();
}
}
synchronized 메소드 방식 을 사용해보자
package thread;
// synchronized 메소드 방식
class Bank2 {
private int money = 10000;
public synchronized void saveMoney(int save) {
// 메소드에다가 synchronized 동기화 메소드로 지정해주면 된다.
// 요 메소드가 속해있는 saveMoney 수행시 Bank2 에 접근을 못하게 된다.
int m = this.getMoney();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setMoney(m + save);
}
public synchronized void minuMoney(int minus) {
int m = this.getMoney();
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setMoney(m - minus);
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
}
class Park2 extends Thread {
// 출근
public void run() {
// 돈을 저금한다
System.out.println("start save");
SyncTest2.myBank.saveMoney(3000);
System.out.println("save money" + SyncTest2.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
class ParkWife2 extends Thread {
public void run() {
// 돈을 사용한다.
System.out.println("start minus");
SyncTest2.myBank.minuMoney(1000); // 천원저금
System.out.println("minus money" + SyncTest2.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
public class SyncTest2 {
public static Bank2 myBank = new Bank2(); // 은행 하나 생성 , static 으로 사용해서 클래스로 접근 가능
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Park2 p2 = new Park2();
p2.start();
Thread.sleep(200); // Park 이 저축하고나서 0.2초 후에 와이프가 시작
// synchronized로 인해 Park이 수행이 다끝나기 전에 와이프는 Bank 에 접근할수없게된다.
ParkWife2 pw2 = new ParkWife2();
pw2.start();
}
}

1000원을 소비한 후의 가격이다. - 동기화
synchronized 블록 방식도 있다.
package thread;
// synchronized 블록 방식
class Bank3 {
private int money = 10000;
public synchronized void saveMoney(int save) {
// synchronized 블록 방식
synchronized(this) { // 어느 객체에 락을 걸것인가. this 즉 요 객체 Bank3 에다가
int m = this.getMoney();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setMoney(m + save);
}
}
public synchronized void minuMoney(int minus) {
int m = this.getMoney();
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setMoney(m - minus);
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
}
// run 에다가 synchronized 를 걸어도 백날 소용이 없다.
// 락을 걸고 싶다면 synchronized 블록 방식으로 건다.
class Park3 extends Thread {
// 출근
public void run() {
synchronized(SyncTest3.myBank) { // 객체를 넣는다.
// 즉 이 객체가 수행하는동안 이 객체는 락이 걸린다.
System.out.println("start save");
SyncTest3.myBank.saveMoney(3000);
System.out.println("save money" + SyncTest3.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
}
class ParkWife3 extends Thread {
public void run() {
synchronized(SyncTest3.myBank) { // 객체를 넣는다.
System.out.println("start minus");
SyncTest3.myBank.minuMoney(1000); // 천원저금
System.out.println("minus money" + SyncTest3.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
}
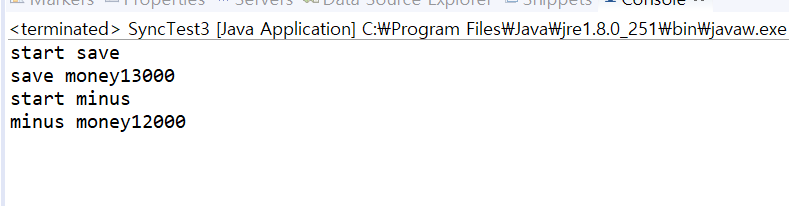
public class SyncTest3 {
public static Bank3 myBank = new Bank3(); // 은행 하나 생성 , static 으로 사용해서 클래스로 접근 가능
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Park3 p3 = new Park3();
p3.start();
Thread.sleep(200); // Park 이 저축하고나서 0.2초 후에 와이프가 시작
// synchronized로 인해 Park이 수행이 다끝나기 전에 와이프는 Bank 에 접근할수없게된다.
ParkWife3 pw3 = new ParkWife3();
pw3.start();
}
}