JAVA Programming
[52] equals() 와 hashCode() 재정의
꾸준히개발하자
2020. 7. 17. 14:42
package object;
class Student {
public int studentNum;
public String studentName;
public Student(int studentNum , String studentName) {
this.studentNum = studentNum;
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Student) { // Object 가 Student 의 객체 타입인지 확인한다.
Student std = (Student) obj; // 이 obj를 다운캐스팅하고나서
if(this.studentNum == std.studentNum) { // studentNum 끼리 비교한다.
return true;
} else
return false;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() { // equals 가 같으면 hashCode값도 동일하게 한다
// equals 에서 쓴 멤버를 이용하면 된다.
return studentNum; // studentNum 값 true , false 를 주면 된다.
}
}
public class EqualsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student Lee = new Student(1000,"이순신");
Student Lee2 = Lee;
Student kim = new Student(1000,"이순신");
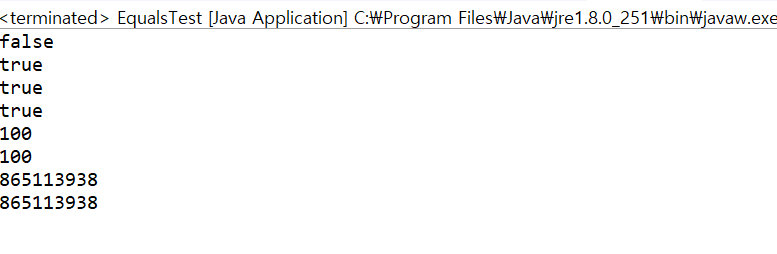
System.out.println(Lee == kim);
System.out.println(Lee.equals(kim));
System.out.println(Lee.hashCode() == Lee2.hashCode()); // true
Integer i1 = 100;
Integer i2 = 100;
System.out.println(i1.equals(i2));
System.out.println(i1.hashCode());
System.out.println(i2.hashCode());
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(i1)); // 실제 가지고 있는 해시코드값
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(i2)); // 실제 가지고 있는 해시코드값
// 해시코드 값은 다르다
}
}hashCode()는 jvm에 인스턴스가 생성됐을 때 메모리 주소를 주는데 그 주소값을 해시코드 라고 한다.
나중에 컬렉션 프레임워크 할 때 설명할 것이다.
10진수의 값이 나온다.